If you feel a tingling when urinating, be suspicious!!! Urethritis.
Causes
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Able to infect in the mouth, the urethra, the prostate, the testicles, the vagina, the cervix, etc.
※ Common infection routes by gender: Male - The urethra, Female - The vagina
- It is classified into gonococcal urethritis and non-gonococcal urethritis depending on the causative
pathogens.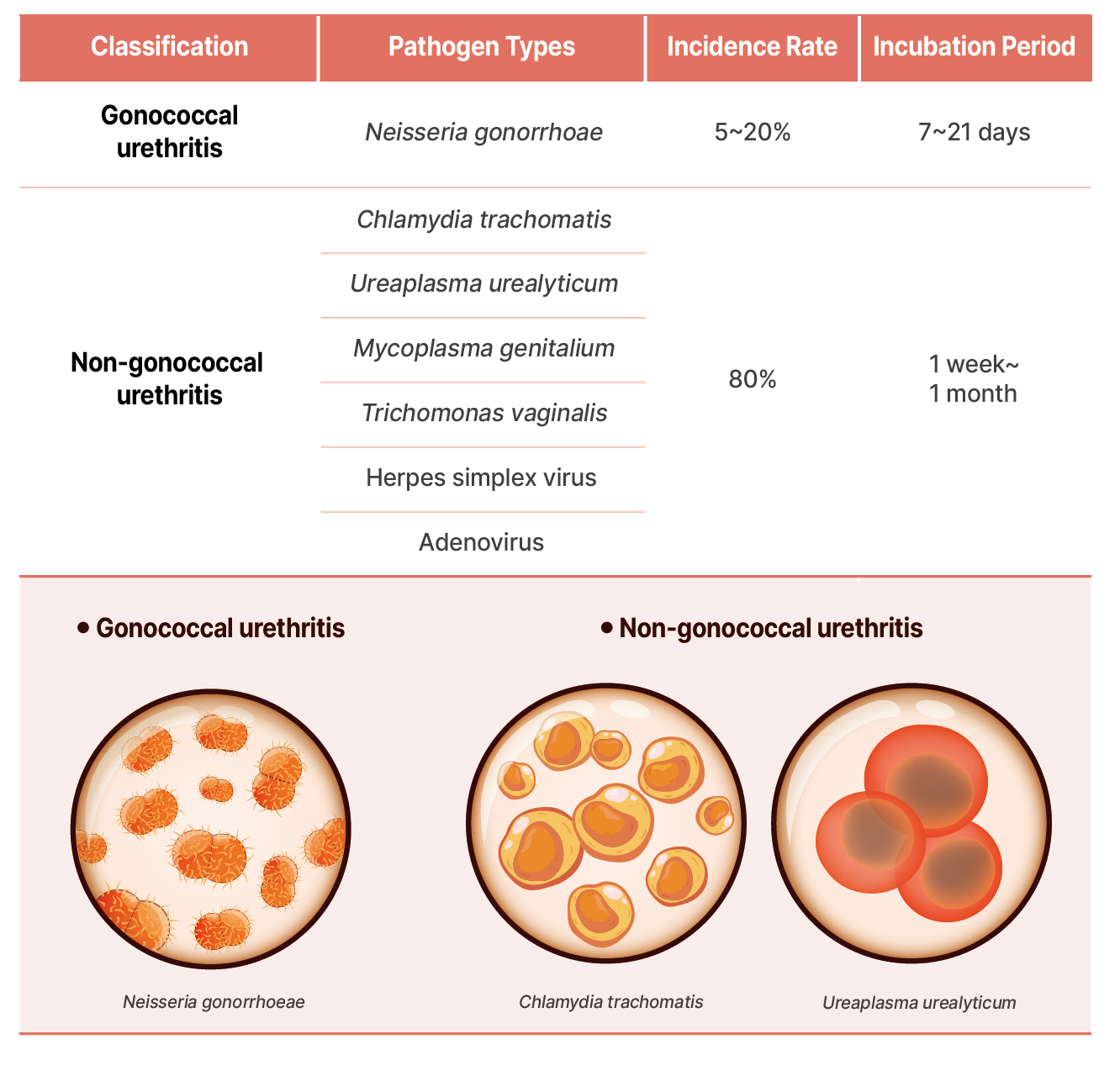
Symptoms
[Male]
- When infected with Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the onset of symptoms is typically within 2-7 days.
- Discomfort and itching in the urethra are common.
- Increased frequency of urination, a tingling pain in the urethra, and the feeling of stuck urethral opening
due to discharge.
- Discharge resembling pus is expelled through the urethra.[Female]
- Unlike males, most cases have no symptoms.
- Increased vaginal discharge and itching of the external genitalia.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding may occur.
- Pain or a burning sensation during urination can be present.
- Lower abdominal pain or pain during sexual intercourse may occur.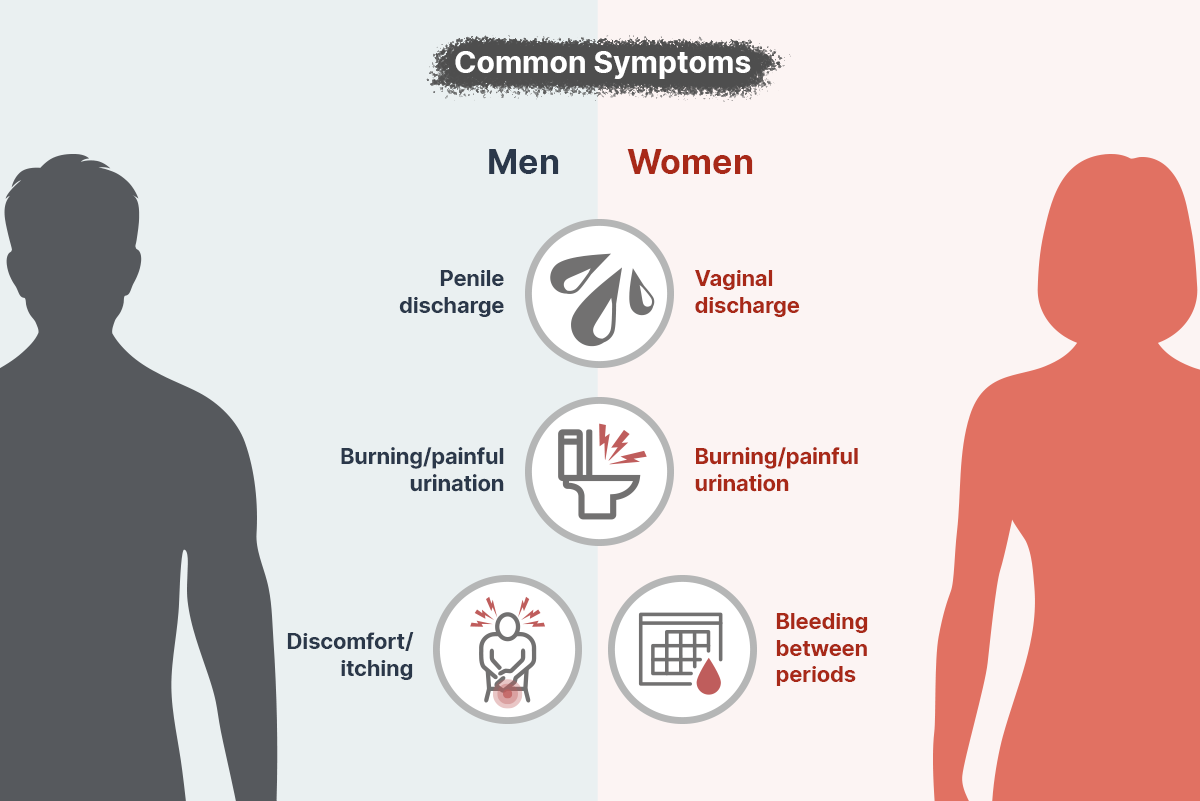
Diagnosis
[Bacterial culture test]
- Observed Gram-negative diplococci in cells when microscopy of specimens
(Blood and samples from the urethra or the cervix)
- Identification of gonococcal urethritis and non-gonococcal urethritis from specimens
(Blood and samples from the urethra or the cervix)[PCR test]
- Detection of specific antigens and genes from specimens
(Urethral, cervical and vaginal smears and first-void urine)Prevention Methods
1. Essential to practice healthy and good sexual hygiene, including the use of condoms during sexual
intercourse.
2. If a sexual partner is infected, treatment is crucial for prevention.
3. Sufficient hydration and avoiding holding urine.
4. Regular check-ups and screenings for early detection.Medical Status
According to statistics from the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service in the Republic of Korea, the number of individuals who were treated to "other urethritis" (Diagnosis code, N34.2) in 2021 was 154, 670 people.
By age group, individuals in 20s accounted for 31.7% of the treated population, followed by 30s of 29.5%, and 40s of 15.8%.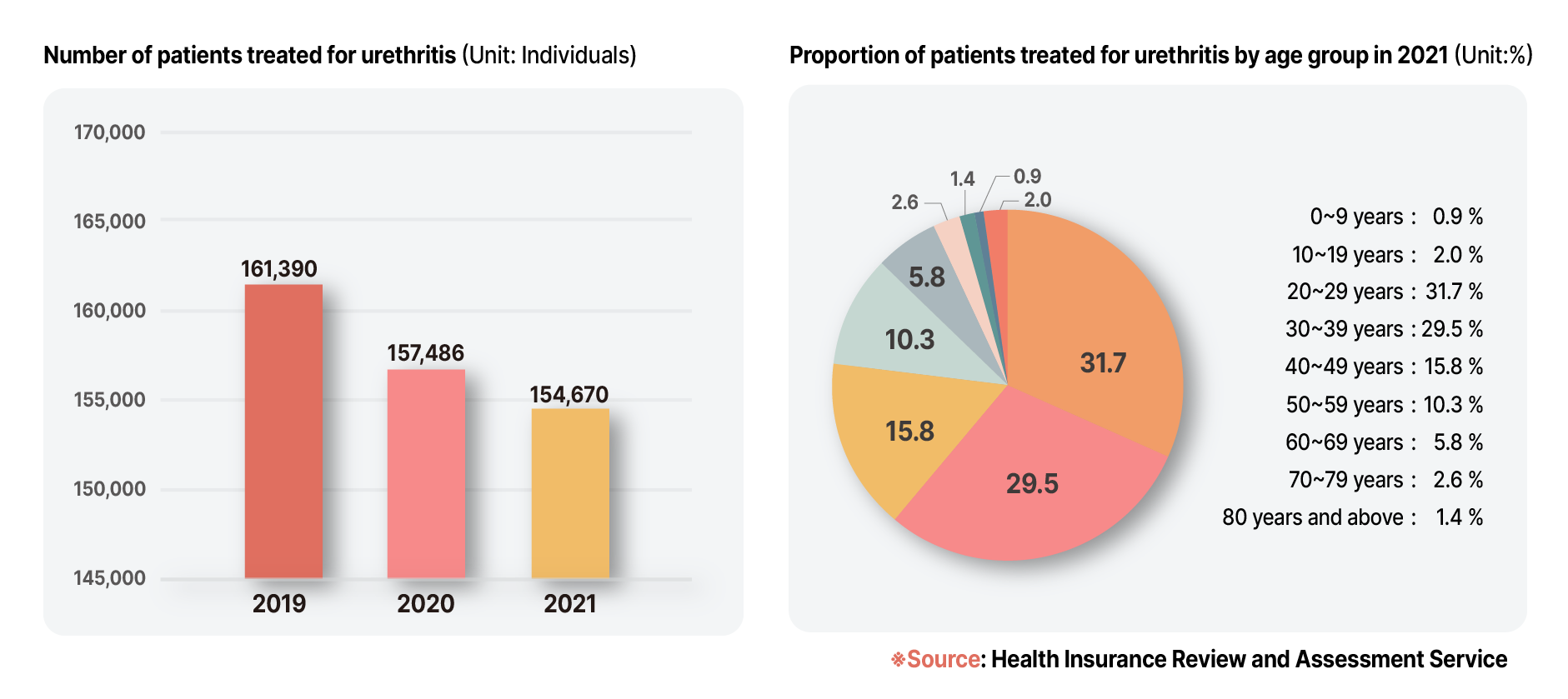
Follow us on social media
